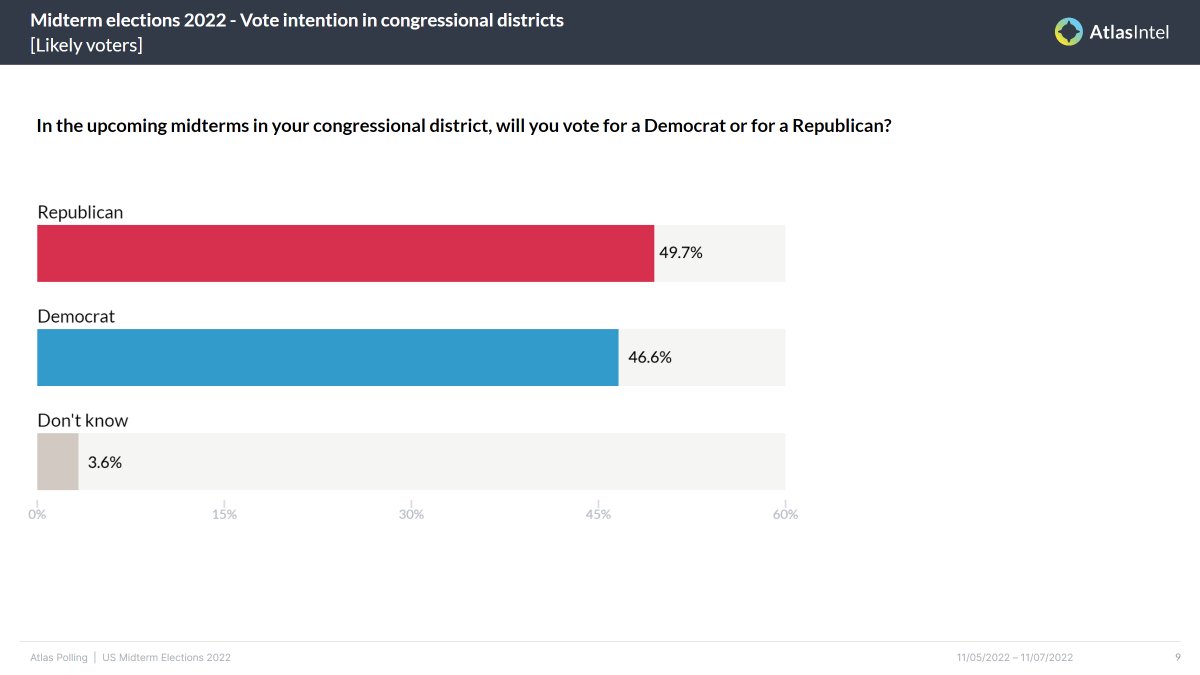
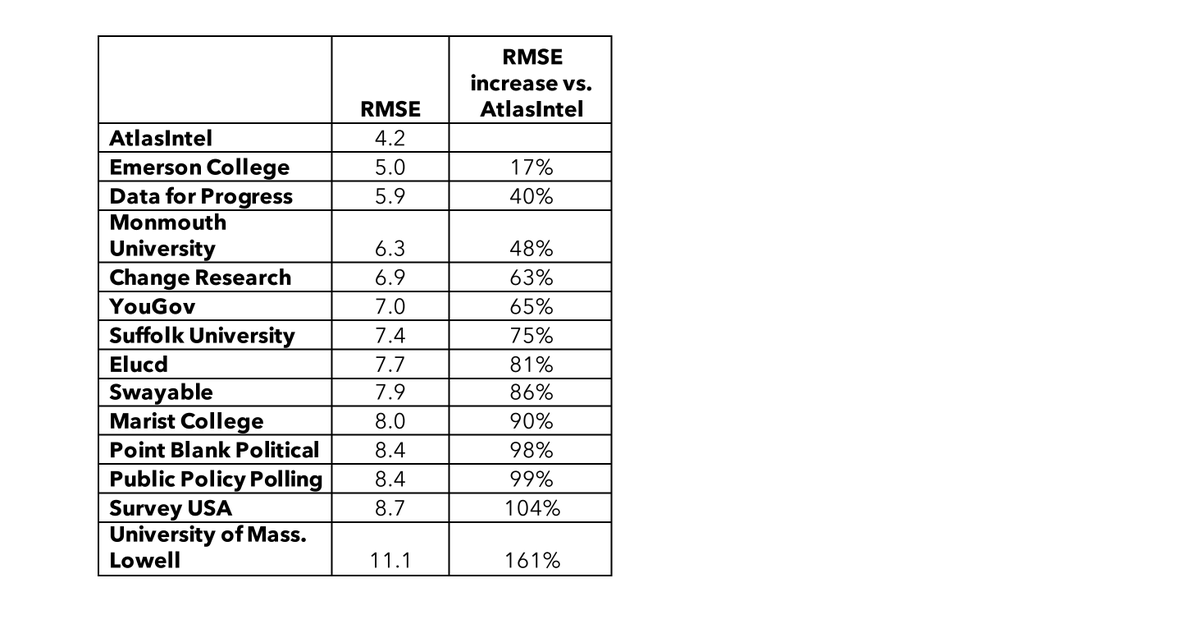
In today's data-driven world, polling has become an essential tool for understanding public opinion and predicting outcomes. However, atlas intel polling bias can significantly affect the accuracy and reliability of these polls, leading to misleading conclusions. As businesses, governments, and organizations increasingly rely on polling data to make critical decisions, understanding the nuances of polling bias is crucial for ensuring informed and effective strategies.
Polling bias refers to the systematic errors that occur during the data collection and analysis process, skewing the results and creating an inaccurate representation of public opinion. This bias can arise from various factors, including sampling errors, question wording, and respondent behavior. By exploring the concept of atlas intel polling bias, we can gain a deeper understanding of its implications and develop strategies to mitigate its effects.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various aspects of atlas intel polling bias, examining its causes, consequences, and potential solutions. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how polling bias impacts decision-making and how to address it effectively. Let's dive in!
Read also:Who Plays Flo On Progressive Commercials The Ultimate Guide To Her Career Personality And Impact
Table of Contents
- What is Atlas Intel Polling Bias?
- Common Types of Polling Bias
- Effects of Polling Bias on Decision-Making
- Sampling Methods and Their Role in Bias
- Question Design and Bias
- Respondent Behavior and Bias
- Technology and Polling Bias
- Mitigating Polling Bias
- Case Studies of Polling Bias
- Future Directions for Polling Methodology
What is Atlas Intel Polling Bias?
Atlas intel polling bias refers to the systematic errors that occur during the polling process, leading to inaccurate or misleading results. These errors can arise from various stages of the polling process, including sampling, question design, and data analysis. Polling bias can significantly affect the reliability of polling data, making it essential to identify and address these issues.
Polling bias is not a new phenomenon; it has been a topic of discussion among researchers and statisticians for decades. However, with the increasing reliance on polling data for decision-making, understanding the causes and effects of polling bias is more critical than ever. In this section, we will explore the definition of polling bias, its historical context, and its relevance in today's data-driven world.
Common Types of Polling Bias
Sampling Bias
Sampling bias occurs when the sample used in a poll does not accurately represent the population being studied. This can happen due to various reasons, such as non-random sampling, underrepresentation of certain demographic groups, or overrepresentation of others. Sampling bias can significantly affect the accuracy of polling results, leading to misleading conclusions.
Question Wording Bias
Question wording bias arises when the phrasing of a question influences the respondent's answer. This can occur through the use of loaded or leading questions, complex language, or ambiguous terms. By carefully designing questions, pollsters can minimize the risk of question wording bias and improve the reliability of their data.
Nonresponse Bias
Nonresponse bias occurs when certain groups of people are less likely to participate in a poll, leading to an unbalanced sample. This can happen due to factors such as age, education level, or socioeconomic status. Nonresponse bias can skew polling results, making it essential to address this issue through effective sampling strategies.
Effects of Polling Bias on Decision-Making
Polling bias can have significant implications for decision-making, particularly in areas such as politics, marketing, and public policy. When polling data is inaccurate or misleading, it can lead to poor decisions, wasted resources, and unintended consequences. In this section, we will examine the effects of polling bias on various sectors and discuss the importance of accurate polling data for effective decision-making.
Read also:Mastering Architect Hashtags Boost Your Online Presence With Strategic Hashtag Use
- Politics: Polling bias can affect election predictions, voter turnout, and campaign strategies.
- Marketing: Inaccurate polling data can lead to ineffective marketing campaigns and missed opportunities.
- Public Policy: Polling bias can influence policy decisions, affecting the well-being of entire communities.
Sampling Methods and Their Role in Bias
Sampling methods play a crucial role in determining the accuracy and reliability of polling data. By selecting an appropriate sampling method, pollsters can minimize the risk of sampling bias and improve the quality of their data. In this section, we will explore various sampling methods and their potential impact on polling bias.
Probability Sampling
Probability sampling involves selecting a random sample from the population, ensuring that every individual has an equal chance of being included. This method reduces the risk of sampling bias and improves the accuracy of polling data.
Non-Probability Sampling
Non-probability sampling involves selecting a sample based on convenience, judgment, or other non-random criteria. While this method can be useful in certain situations, it increases the risk of sampling bias and should be used with caution.
Question Design and Bias
Question design is a critical factor in minimizing polling bias. By carefully crafting questions, pollsters can reduce the risk of question wording bias and improve the reliability of their data. In this section, we will discuss best practices for question design and provide examples of effective question wording.
- Use clear and concise language.
- Avoid loaded or leading questions.
- Include mutually exclusive response options.
Respondent Behavior and Bias
Respondent behavior can also contribute to polling bias, particularly in cases where individuals provide inaccurate or dishonest answers. This can occur due to social desirability bias, where respondents answer in a way they believe is socially acceptable, or acquiescence bias, where respondents tend to agree with statements regardless of their true opinions. In this section, we will examine the impact of respondent behavior on polling bias and discuss strategies for addressing these issues.
Technology and Polling Bias
Advances in technology have revolutionized the polling industry, offering new opportunities for data collection and analysis. However, these technological advancements can also introduce new forms of polling bias, such as digital divide bias or algorithmic bias. In this section, we will explore the role of technology in polling bias and discuss strategies for mitigating these risks.
Mitigating Polling Bias
Mitigating polling bias requires a multifaceted approach, addressing issues related to sampling, question design, respondent behavior, and technology. By implementing best practices and leveraging advanced statistical techniques, pollsters can improve the accuracy and reliability of their data. In this section, we will provide actionable strategies for mitigating polling bias and enhancing the quality of polling data.
Weighting and Adjustments
Weighting and adjustments involve applying statistical techniques to account for sampling biases and improve the representativeness of the data. This method can help reduce the impact of sampling bias and improve the accuracy of polling results.
Quality Control Measures
Implementing quality control measures, such as pretesting questions and monitoring response rates, can help identify and address potential sources of bias. By maintaining high standards for data collection and analysis, pollsters can ensure the reliability of their data.
Case Studies of Polling Bias
Examining real-world examples of polling bias can provide valuable insights into its causes and effects. In this section, we will explore several case studies of polling bias, highlighting the lessons learned and the strategies employed to address these issues.
The 2016 U.S. Presidential Election
The 2016 U.S. presidential election serves as a prominent example of polling bias, where many polls failed to accurately predict the outcome. This case study highlights the importance of addressing sampling bias and respondent behavior in polling methodology.
The Brexit Referendum
The Brexit referendum provides another example of polling bias, where many polls underestimated the level of support for leaving the European Union. This case study underscores the need for careful question design and sampling methods in polling research.
Future Directions for Polling Methodology
As the polling industry continues to evolve, new methods and technologies offer promising opportunities for improving the accuracy and reliability of polling data. In this section, we will discuss potential future directions for polling methodology, including the use of big data, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
By embracing these advancements and continuing to address the challenges of polling bias, the industry can ensure the continued relevance and effectiveness of polling data in today's data-driven world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, atlas intel polling bias is a critical issue that affects the accuracy and reliability of polling data, with significant implications for decision-making across various sectors. By understanding the causes and effects of polling bias and implementing strategies to address these issues, we can improve the quality of polling data and ensure informed and effective decision-making.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with polling bias in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into data-driven decision-making and polling methodology. Together, we can work towards a more accurate and reliable polling industry for the future.
Data sources: Pew Research Center, Gallup, and American Association for Public Opinion Research.